Contents
Introduction
Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) aka Temporal Arteritis is an immune-mediated inflammatory condition of the medium to large arteries which particularly affects the branches of the carotid artery. It presents with acute onset temporal headache, malaise and fevers. It can cause sudden visual loss, particularly in the elderly.
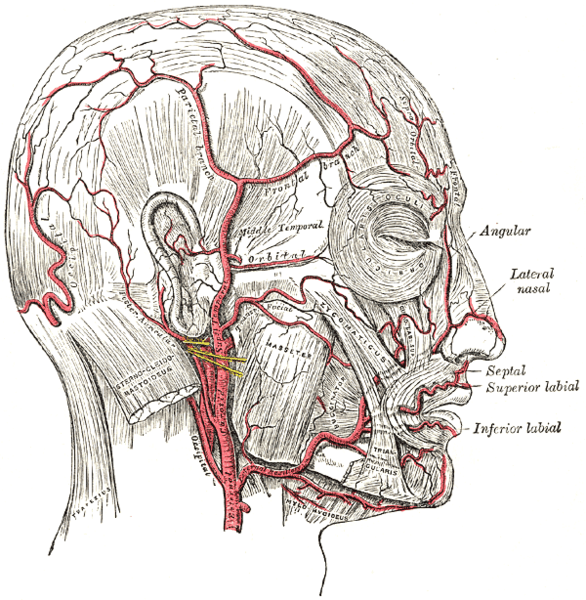
Arteritis is the inflammation of the walls of the arteries. In GCA, inflamed superficial temporal or occipital arteries cause pain. Touching the skin over these vessels (e.g. when combing hair) will cause pain. The vessels may become hardened, and arterial pulsation is lost. The scalp around the arteries becomes thickened and red. It is possible that patches of gangrene occur.
The aetiology is unknown. It is strongly associated with Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) – to the point where some believe that they are different manifestations of the same disease.
Prompt management with corticosteroids can prevent blindness and improve other symptoms.
Epidemiology
- F > M – approx 2 -3 :1
- Higher incidence in Northern European countries
- Usually only seen in patients aged >50
- 20% chance of permanent visual loss
- About 50% of patients also have concurrent polymyalgia rheumatica
- Only about 15% of those with PMR get GCA
- A small percentage of patients also have disease in the large arteries, which can cause intra-thoracic and abdominal manifestations
Clinical features
- Rare under 50
- Generalised headaches
- Scalp tenderness – 25% of cases
- May be apparent when combing hair or resting head on a pillow
- Claudication of the jaw – 25% of cases
- Painless temporary or permanent visual loss – if more than one of the occipital or temporal arteries is affected
- Other visual disturbance may also be apparent, e.g. double vision
- ANY visual disturbance is critical
- Sudden blindness can occur without any of the other symptoms
- Generalised malaise
- Fever
- Tiredness
Examination
- Perform an eye exam
- Visual acuity
- Visual fields
- Eye movements
- Pupillary light reaction
- Perform fundoscopy – check optic disc and retinal vessels
- Examine temporal arteries
- May feel thickened or hardened
- May have absent pulses
- Normal artery examination does NOT exclude the diagnosis
Investigations
Bloods:
- ESR and CRP
- Any elevation of either suggests a diagnosis of GCA
- 5-10% of patients will have normal ESR and CRP – especially those with blindness only
- Normal ESR and CRP makes GCA unlikely but does not rule out the diagnosis
- FBC
- Normocytic / normochromic anaemia
- Platelets may be elevated
LFT’s
- Low albumin
- ↑ALP
- ↑y-GT
Temporal arterial biopsy
- This is the definitive diagnostic test. You should take the sample before or within 7 days of starting steroids (if these are given)
- Histological features include:
- Intimal hypertrophy
- Inflammation of the intima
- Degredation of the internal elastic lamina
- Giant cells, lymphocytes and plasma cells in the internal elastic lamina
Treatment
If suspected GCA – start corticosteroids immediately, and refer to ophthalmology for temporal artery biopsy.
No visual loss
- Prednisolone PO – 40-60mg /day – can be single or divided doses
- This can dramatically reduce symptoms within 24 hours.
- Continue for a minimum of 4 weeks – and at least until symptoms AND inflammatory markers have resolved
- Then – taper the dose
- Reduce daily dose by 10mg every 2 weeks until 20mg daily
- Then reduce by 2.5mg every 2 weeks until 10mg daily
- Then reduce by 1mg daily every 2 weeks
- Continue until steroids have ceased, provided no relapse of symptoms
- Dose adjustments are often guided by specialist
- Methotrexate may be considered as an adjunct in patients who do not respond will to steroids
- Start low dose aspirin – 100mg daily PO
- This reduced the risk of a thrombotic event in the affected arteries
- Follow up:
- After 2-3 days
- At 1, 3 and 6 weeks
- Every 3 months if on continuing treatment
- Manage relapses by initially increasing to the previous dose of prednisolone. If symptoms severe – return to the starting dose.
Visual loss
- IV methylprednisolone 0.5 – 1g daily for three days
- Then switch to oral prednisolone and other measures as above
Other factors
- The disease is likely to settle after 12-36 months of treatment in 75% of cases. In the remaining 25%, low dose corticosteroids may be needed for years.
- Calcium and vit D supplements should be given to avoid osteoporosis whilst on steroids.
- Consider PPI for gastric protection if patient is at increased risk of GI bleeding or dyspepsia
NSAID’s should not be used.
References
- Murtagh’s General Practice. 6th Ed. (2015) John Murtagh, Jill Rosenblatt
- Oxford Handbook of General Practice. 3rd Ed. (2010) Simon, C., Everitt, H., van Drop, F.
- Beers, MH., Porter RS., Jones, TV., Kaplan JL., Berkwits, M. The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy
- Giant Cell Arteritis – patient.info
- Giant Cell Arteritis (Temporal Arteritis) – Health Pathways